Gout is the most common type of inflammatory arthritis, and risk increases with age, It results from the build-up of excess uric acid in the body, which forms crystals that deposit in small joints or soft tissues and cause inflammation and pain. In people who have gout, uric acid production is increased while its elimination is reduced.
Uric Acid and Hyperuricemia?
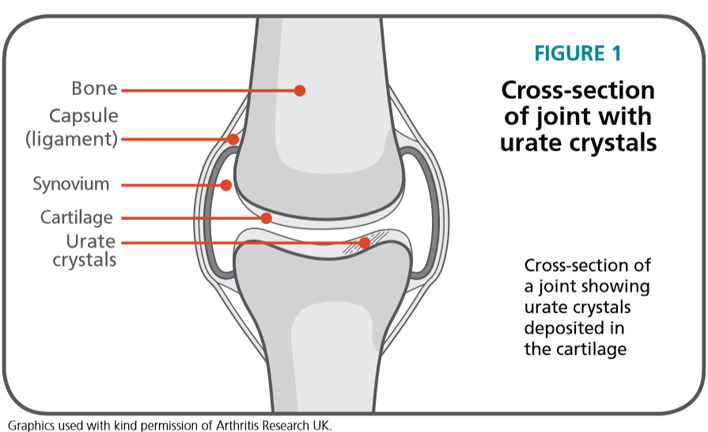
Uric acid is present in small amounts in our blood. It is produced when the body breaks down a chemical called purine. Purines are either made by your body, or taken into your body through foods you eat. The uric acid travels to the kidneys where most is removed from the body as waste in urine. However, people with gout have higher-than-normal amounts of uric acid in their bloodstream. This condition is what we call hyperuricemia. Unfortunately, If uric acid reaches 7 mg/dL or higher, needle-like crystals of monosodium urate monohydrate (MSU) forms in joints to create what we all know as gout.(Refer figure 1 ).
What Are The Symptoms of Gout?
Symptoms of gout depend on the stage of the disease. But common symptoms include severe joint pain, usually with redness, swelling, and tenderness of the joint. The pain is likely to be most severe within the first four to 12 hours after it begins. The progression of gout is divided into the following four stages:
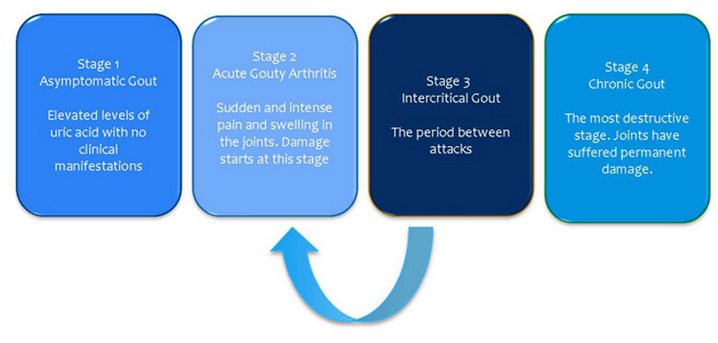
Asymptomatic hyperuricemia
Acute gouty arthritis
Intercritical gout
Chronic tophaceous gout
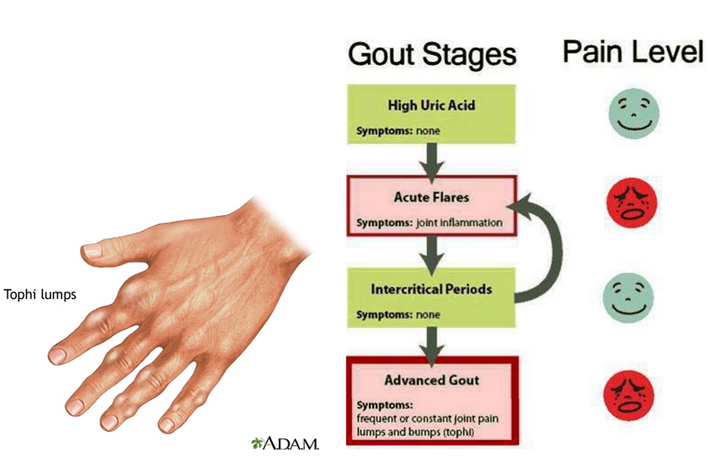
Asymptomatic Hyperuricemia
Uric acid accumulates in the blood in the first stage of gout, causing a condition known as hyperuricemia. Asymptomatic means there are no symptoms. But you have to notice that increase in blood uric acid is still harmful. This stage may last 30 years or more.
Acute Gout
Acute gouty arthritis occurs when excess uric forms sodium urate crystals that collect in joint spaces. Symptoms of acute gout often start in one joint and usually develop very rapidly within 6 to 24 hours. It can strike suddenly and often occurs at night. Besides pain, redness, swelling, and warmth over the joint. Chills,fever and loss of appetite appear in general.
Intercritical Gout
Intercritical gout refers to describe the time periods between gout attacks. You will usually experience a complete remission of symptoms period after first attack.. But, the uric acid crystals continue to accumulate quietly,which eventually leads to another attack. Over 67% patients will suffer a second attack within 6 months to 2 years. By 10 years, over 90% of patients are likely to have more attacks.
Chronic Tophaceous Gout
This is the final and the most disabling stage of gout, and it is usually develops over a long period of time without proper treatment. In this stage, large amount of uric acid crystals called tophi produces in the joints, cartilage, bones, and elsewhere in the body. In some cases, tophi break through the skin and appear as white or yellowish-white, chalky nodules. Tophi can cause chronic pain, joint destruction, damage surrounding tissues, and cause deformities, most importantly, it can leads to some complication such as kidney damage.
source from A.D.A.M
Source http://www.nhs.uk/Conditions/Gout/Pages/Symptoms.aspx http://www.crwf.com/four-stages-of-gout/
How to Diagnosis?
There are a few tests are needed to confirm the diagnosis and rule out other possible causes.
Blood tests : A blood test known as a serum uric acid test may be used to measure the amount of uric acid in your blood. Since uric acid level can increase and fall during an attack, it is better to wait until several days after an attack to carry out a blood test. You may need to have blood tested more than once for accuracy.
Synovial fluid test: Synovial fluid surrounds and protects your joints. A sample of fluid may be collected from the affected joint . The fluid is sent to a lab to check for uric acid crystal under a microscope.
Radiographs: An X-ray is primarily used to help rule out similar causes of joint inflammation such as chondrocalcinosis (a build-up of calcium crystals in the joints) or to assess underlying joint damage due to multiple episodes of gout attack.
Health Problems and Complications
Acute gout can cause pain, redness and stiffness, however, many people experience one attack will have a second one. Are you aware of the complications associated with gout? Besides disfiguring damage to joints, Chronic gout can lead to more severe health problems.
Joints Damage. If untreated, gout attacks may become more frequent and prolonged. The inflammation caused by these gout attacks develop permanent joint damage. Eventually, the affected joints can come out of alignment and be rendered completely immobile.
Development of tophi. Uric acid crystals may begin to be deposited in soft tissue, forming white or yellowish lump called tophi. Joints can become deformed whereby you can become disabled. Tophi commonly appear under skin, but they can appear almost anywhere on the body such as ear or elbow. If there is tophi below your skin, there is even more within the cartilage and bone of your joints! Tophi is obviously a sign that you have severe gout and must treat it with proper medication.
Kidney stones are one of complications. Uric acid is normally eliminated by the kidney, for those with gout, excess uric acid forms stones in the kidney, which create blockage in the urinary tract. High concentrations of urate kidney stones can interfere with kidney function.
The frequent co-existence of gout and heart disease has been noted for years. Gout increases the risk of heart disease and stroke. New research published in the Rheumatology journal has found that having gout doubles the risk of heart attack and stroke. The research tracked the health of more than 205,000 gout patients using data spanning five decades to determine relationship between gout and heart attack and stroke. The findings showed that gout patients are twice as likely to suffer a heart attack or stroke as those without gout. It is thought that the higher levels of uric acid which cause gout are also a strong risk factor for heart attack and stroke.
(Source: http://www.rheumatology.org.uk/)
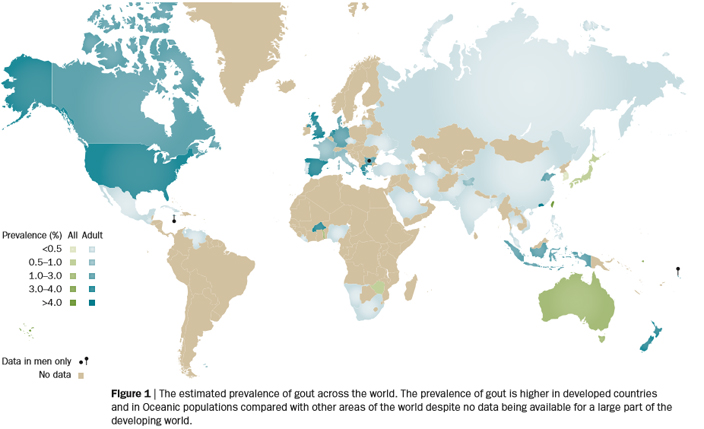
Prevalence
Data from several studies suggest that prevalence of gout continues to increase. Estimates from United States National Health and Nutrition Examination Survey( NHANES) showed that USA prevalence more than doubled in the last half of the twentieth century. And further study estimated that prevalence of gout among US adults was 3.9% or 8.3 million individuals. Among men, the prevalence was 5.9% and among women 2%. Kuo et al. (2015) highlights prevalence of gout worldwide ranges from 0.1% to approximately 10%, and the incidence from 0.3 to 6 cases per 1000 person-years. Both prevalence and incidence of gout are increasing in many developed courtries. But in some oceanian countries, particularly within ethnic groups such as Taiwanese aboriginals and Maori, in which estimates are >10%. Although no formal survey has been undertaken in Canada, gout is generally thought to affect 3& of adults. Uk estimates approximately 2.49% in the entire population.
Risk Factors
Men are significantly at higher risk for gout, primarily because uric acid levels rise substantially at puberty. After menopause, however, women’s uric acid level increase to those of men. Men also are more likely to develop gout earlier than women— usually experience their first attack between the ages of 30 and 50.— whereas women generally develop signs and symptoms after menopause.
Obesity
An increase in Body Mass Index (BMI) or body fatness, waist circumference, and chest circumference poses a significant risk for hyperuricemia and gout. Overweight causes your body to produce more uric acid and kidney has problem in eliminating.
Genetics. Many people with gout have a family history of the disease.
Diet and alcohol intake
People who love drink alcohol keep body from removing uric acid. As alcohol is metabolized to lactate, which contributes to the retention of urate (the salt version fo uric acid). Alcohol such as red wines and beer are high in purines. Purine breaks down to uric acid which increase risk of gout. Patients with gout should avoid foods high in purine such as sea foods and Please check our LIVING PART for more information.
Other health Condition
A number of disease have a strong association with gout. Components of the metabolic syndrome have been associated with hyperuricemia. Renal insufficiency is a common cause of gout in older people. Other health problems that contribute to high blood levels of uric acid include hypertension, diabetes, heart disease and hypothyroidism (underactive thyroid gland),high cholesterol.
Treatments
Once patients have been diagnosed with gout, proper treatments are able to control their symptoms and live productive lives.
The goals for treatment are to ease the pain that comes from sudden attacks, prevent future attacks, stop uric acid buildup in the tissues and joint space between two bones, and prevent kidney stones from forming.
Treatment of acute attacks includes:
Non-steroidal anti-inflammatory drugs (NSAIDs, such as ibuprofen or naproxen) taken by mouth. NSAIDs reduce inflammation but have no effect on the amount of uric acid in the body.
Corticosteroids, such as prednisone, taken either orally or injected into the affected joint. With corticosteroids, patients often begin to improve within a few hours and attacks usually end within a week.
When NSAIDs or corticosteroids fail to control pain and swelling, the doctor may use another drug, colchicine. But it must be taken within the first 12 hours of an acute attack for effectiveness.
Even if drugs like these could cure gout, and there is little, if any, evidence they can, you still would have to deal with some very nasty side effects, it is better to go for natural options for gout. Diet plan is playing a very important role in controlling symptoms.The primary dietary goal for gout is to limit your intake of foods with high amounts of purine in them. Foods considered high in purine content include: seafood, alcohol beverages, some peas.

